All ants’ species members live in colonies with one to many queens, immature, numerous sterile female workers and occasionally males.
Ants can be a threat to human health. Their presence under certain situations can pose a serious human health Risk, i.e. in food processing plants, food preparation areas, food packaging plants, because of the potential for disease transmission.
Ants are sometimes dangerous because of their bites or stings (e.g. Samsoom ants).in United Arab Emirates.
Now, some areas in Dubai show infestation of fire ants.
 |
 |
 |
Ant biology and life cycle
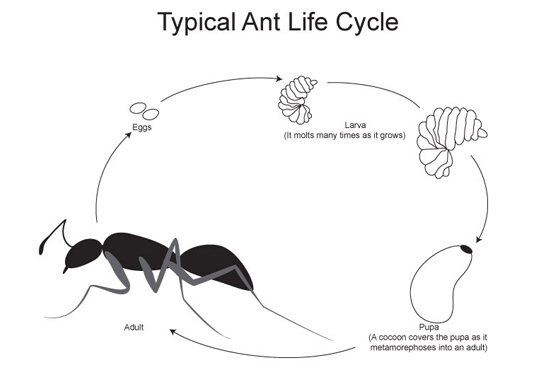
Ant biology facts Ants are social insects that live in colonies that may include thousands of individuals. Ants, along with bees and wasps, are members of the order Hymenoptera and undergo complete metamorphosis passing through four stages:
- Egg
- Larva
- Pupa
- Adult
the wingless worker ants are the most common adults seen. However, there are three types of adults:
- Queens
- Males
- Workers
 |
 |
New Colonies can begin with mated flights:
A new ant colony usually begins as a new queen flies off from an old colony, mates with a male, finds a suitable site, drops her wings and excavates a nest, and cloisters herself within the nest for several weeks or more until her eggs mature. She lays her eggs within the nest, cares for her young, seldom or never leaving the nest again, relying on workers to groom her and feed the colony after the first generation is reared.
Some colonies are established through budding:
For some ant species, such as the Argentine ant and the ant, queens mate in the old nest and workers accompany the new queens to new nesting sites. In these cases, queens may not have wings or be able to fly well. Workers can also establish new colonies with or without mature queens through budding. Workers carry immature stages (eggs, larvae, pupae) to another nest site and rear some of the immature up as reproductive males and females.
Many of the most serious ant pests, including Argentine ant, pharaoh ant, and the carpenter ant, have multiple queens within colonies. Others, such as pavement ants, have only one functional queen. After one season or a few years, depending on the ant species, a colony begins to produce reproductive that leave the colony, often in swarms, to form new colonies. Only a few of the thousands of queens produced are successful in founding a colony.
Preventive Measures:
The Key to Ant Control is Sanitation
- Clean up spills and crumbs.
- If possible, rinse food & drink containers before recycling or disposal.
- Use tight fitting plastic containers for storage.





